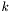 ticks, a BigStep by
ticks, a BigStep by 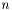 Steps and a SuperStep by
Steps and a SuperStep by 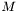 BigSteps.
BigSteps.
#include <detime.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| DETime () | |
| Default Constructor, set the DETime to 0. | |
| DETime (string A) | |
| Set up a new DETime given a string. The string is parsed as seconds. | |
| DETime (time_int _tick, int _PrintMask=DefaultPrintMask) | |
| Set up a new DETime given is parameters. | |
| DETime (const DETime &A) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| DETime (time_int _step, time_int _bigStep, time_int _superStep) | |
| Set up a new DETime from absolute indications about its Steps, BigSteps and SuperSteps. | |
| DETime (double A, int _PrintMask=DefaultPrintMask) | |
| Set up a new DETime from a double. The argument is considered as expressed in seconds. | |
| time_int | Tick () const |
| returns the absolute tick of the time represented. | |
| time_int | Step () const |
| returns the absolute Step index of the time represented. | |
| time_int | BigStep () const |
| returns the absolute BigStep index of the time represented. | |
| time_int | SuperStep () const |
| returns the absolute SuperStep index of the time represented. | |
| time_int | RelativeTick () const |
| returns the Tick index relative to the beginning of the Step. | |
| time_int | RelativeStep () const |
| returns the Step index relative to the beginning of the BigStep. | |
| time_int | RelativeBigStep () const |
| returns the BigStep index relative to the beginning of the SuperStep. | |
| DETime | operator= (const DETime &A) |
| Assignement operator. | |
| DETime | operator+ (const DETime &A) const |
| Plus operator. | |
| DETime | operator+ (const time_int A) const |
| Plus operator. Note that a time_int is a time expressed in ticks. | |
| DETime | operator+ (const double A) const |
| Plus operator. Note that the double value means seconds. | |
| DETime | operator+= (const DETime &A) |
| Plus Equal operator. | |
| DETime | operator+= (const time_int A) |
| Plus Equal operator. Note that a time_int is a time expressed in ticks. | |
| DETime | operator- (const DETime &A) const |
| Minus operator. It checks if the resulting DETime is negative and abort the simulation if so. | |
| DETime | operator- (const time_int A) const |
| Minus operator. It checks if the resulting DETime is negative and abort the simulation if so. Note that a time_int is a time expressed in ticks. | |
| DETime | operator * (const time_int A) const |
| Multiplication operator. Note: the 2nd operator is a pure number. DETime(2.0)*time_int(2) == DETime(4.0). | |
| DETime | operator * (const double A) const |
| Multiplication operator. Note: the 2nd operator is a pure number. DETime(2.0)*double(2.5) == DETime(5.0). | |
| DETime | operator/ (const time_int A) const |
| Division operator. Note: the 2nd operator is a pure number. DETime(2.0)/time_int(2) == DETime(1.0). | |
| const time_int | operator/ (const DETime &A) const |
| Division operator. DETime(4.0)/DETime(2.0) == 2. | |
| time_int | operator% (const time_int A) const |
| Modulus operator. DETime(1.0)time_int(2) == ??? depends on how many ticks is 1 second. | |
| bool | operator< (const DETime &A) const |
| operator < . Compares the ticks only of two DETimes. | |
| bool | operator> (const DETime &A) const |
| operator > . Compares the ticks only of two DETimes. | |
| bool | operator<= (const DETime &A) const |
| operator <= . Compares the ticks only of two DETimes. | |
| bool | operator>= (const DETime &A) const |
| operator >= . Compares the ticks only of two DETimes. | |
| bool | operator== (const DETime &A) const |
| operator == . Compares the ticks only of two DETimes. | |
| bool | operator!= (const DETime &A) const |
| operator != . Compares the ticks only of two DETimes. | |
| DETime | AddStep () const |
| returns the time represented plus 1 Step. Equivalent to AddStep(1) (but faster). | |
| DETime | AddStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time represented plus S Steps | |
| DETime | AddBigStep () const |
| returns the time represented plus 1 BigStep. Equivalent to AddBigStep(1) (but faster). | |
| DETime | AddBigStep (time_int BS) const |
| returns the time represented plus BS BigSteps | |
| DETime | AddSuperStep () const |
| returns the time represented plus 1 SuperStep. Equivalent to AddSuperStep(1) (but faster). | |
| DETime | AddSuperStep (time_int SS) const |
| returns the time represented plus SS SuperSteps | |
| DETime | NextStep () const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next Step. Equivalent to NextStep(1) (but faster). | |
| DETime | NextStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next Step plus (S-1) Steps. | |
| DETime | NextBigStep () const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next BigStep. Equivalent to NextBigStep(1) (but faster). | |
| DETime | NextBigStep (time_int BS) const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next BigStep plus (BS-1) BigSteps. | |
| DETime | NextSuperStep () const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next SuperStep. Equivalent to NextSuperStep(1) (but faster). | |
| DETime | NextSuperStep (time_int SS) const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next SuperStep plus (SS-1) SuperSteps. | |
| DETime | NextIndexedStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next Step whose index within the actual BigStep is S. | |
| DETime | NextIndexedBigStep (time_int BS) const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next Step whose index within the BigStep is the actual one and the index of the BigStep is BS. | |
| DETime | BeginOfTheNextUsefulStep (void) const |
| returns the time representing the beginning of the next Step, or this time if it's already a Step begin. | |
| DETime | ToNextStep () const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next Step. Equivalent to A.NextStep() - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next Step plus (S-1) Steps. Equivalent to A.NextStep(S) - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextBigStep () const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next BigStep. Equivalent to A.NextBigStep() - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextBigStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next BigStep plus (BS-1) BigStep. Equivalent to A.NextBigStep(BS) - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextSuperStep () const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next SuperStep. Equivalent to A.NextSuperStep() - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextSuperStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next SuperStep plus (SS-1) BigStep. Equivalent to A.NextSuperStep(SS) - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextIndexedStep (time_int S) const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next Step whose index within the actual BigStep is S. Equivalent to A.NextIndexedStep() - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToNextIndexedBigStep (time_int BS) const |
| returns the time needed to reach the beginning of the next Step whose index within the BigStep is the actual one and the index of the BigStep is BS. Equivalent to A.NextIndexedBigStep() - A (but faster). | |
| DETime | ToBeginOfTheNextUsefulStep (void) const |
| returns the time needed to syncronize with the start of the next Step, or this time if it's already a Step begin. Equivalent to A.BeginOfTheNextUsefulStep() - A (but faster). | |
| bool | HasOffsetZero () const |
| returns true if the time is at the begin of a Step. | |
| bool | IsInOverFlow () const |
| returns true if the time is in overflow. | |
| operator double () | |
| converts a DETime to a double; used for printing a DETime. Try to avoid other uses. | |
Friends | |
| ostream & | operator<< (ostream &os, const DETime &t) |
| prints the time represented by t in the format specified by PRINTMASK. | |
The Time in NePSing is represented via the DETime class. This class offers a number of facilities for convert, order, manipulate and print the Time in order to make it easier to program a generic time-oriented simulation. In particular it offers a framed structure that can be used in any TDMA-based communication protocol.
The time is internally stored as an unsigned long long int (usually 64 bits).
The time structure can be divided into ticks, Steps, BigSteps and SuperSteps, each one multiple of the other. hence, a Step will be made by 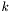 ticks, a BigStep by
ticks, a BigStep by 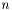 Steps and a SuperStep by
Steps and a SuperStep by 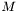 BigSteps.
BigSteps.
A particular attention must be devoted to the way of reading and writing a DETime. In order to not loose precision while not messing up with time internals, a DETime can be expressed also by a double precision number. This number will be converted into a DETime with a rather complex parsing function; hence, it is discouraged to express DETimes as a double in the user's code.
In order to read and write a DETime in a 'human readable' format, e.g., 3.5 seconds, the concept of resolution is used. The resolution is expressed with an (usually) negative integer number, indicating the numeber of digits past the dot that NePSing will consider as significative. As an example, a resolution of -6 means that NePSing base time will be expressed in milliseconds (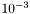 seconds), and the minimum representable time will be 1 millisecond (i.e., 1 tick).
seconds), and the minimum representable time will be 1 millisecond (i.e., 1 tick).
Note that the assocation between DETime(1.0) and 1 second is only a convention, as it is possible to consider DETime(1.0) as 1 day, as NePSing knows nothing about the real meaning of a second.
 1.3.9.1 ---- Hosted
by
1.3.9.1 ---- Hosted
by